Introduction to supply chain finance
Supply chain finance offers a lifeline to companies looking to optimize their working capital and streamline their financial processes. At the same time, today’s competitive landscape demands knowledge of the intricacies of supply chain financing to stay ahead of the curve.
However, navigating the realm of supply network finance can be daunting. Businesses can grapple with complex financial challenges that hinder their growth and profitability. Organizations face numerous hurdles, from managing cash flow gaps to mitigating supplier risks.
Fortunately, this guide sheds light on logistics finance’s core concepts and strategies. So, let’s look at actionable insights and practical solutions to help you navigate the world of logistics financing.
Read More: TOP 10 Procure-to-Pay Software Solutions in 2023
What is supply chain finance (SCF)?
Supply chain finance is a specialized form of financing that focuses on optimizing cash flow within the supply chain ecosystem. It enables businesses to unlock the value trapped in their supply chain by facilitating early payment to suppliers in exchange for certain benefits.
In traditional procurement dynamics, there is often a mismatch between the payment terms negotiated with suppliers and the time businesses take to generate revenue from goods or services. A misalignment can create cash flow gaps and financially strain buyers and suppliers.
Logistics finance offers a solution to this problem through a financial arrangement that benefits all parties involved. Collaborating with financial institutions or third-party trade finance providers allows buyers to extend their payment terms while offering their suppliers the option to receive early payment. The win-win mechanism enables suppliers to improve their cash flow and get lower financing costs.
Quick read: 10 Best Purchase Order Software in 2023
Importance of supply chain finance in optimizing cash flow
Effective cash flow management is crucial for any business’s financial health and sustainability. Utilizing logistics finance allows organizations to address cash flow gaps and enhance liquidity within their supply chain network. It enables enterprises to get immediate payment, ensure sufficient funds to meet operational expenses and invest in growth opportunities.
Additionally, logistics finance fosters collaboration and trust between buyers and suppliers, leading to stronger partnerships and more favorable credit terms. Optimizing cash flow through supply network finance empowers businesses to achieve better financial stability and seize growth opportunities.
Learn more: 10 Best Purchasing Software for Organizations
Benefits of supply chain finance
Supply chain financing offers the following benefits that contribute to businesses’ financial health and operational efficiency. Let’s understand each with an example.
- Improved working capital management: A clothing retailer may extend payment terms to its apparel suppliers from 30 to 60 days. It enables the retailer to retain cash for other operational needs while providing suppliers with the necessary funds to continue production and meet demand.
- Enhanced liquidity and cash flow optimization: A technology manufacturer offers its component suppliers the opportunity to receive early payment at a discounted rate. It helps suppliers improve liquidity and bridge cash flow gaps.
- Strengthened relationships between suppliers and buyers: An automobile manufacturer implements a supplier financing program allowing suppliers to access affordable financing options. It demonstrates the manufacturer’s commitment to supporting the financial stability of its suppliers.
Suggested Read: 6 Best Cash Flow Management Software
Different types of supply chain finance programs
Supply network finance programs come in various forms, offering businesses flexibility in optimizing their financial operations. Here are some common types:
1. Reverse factoring
In this arrangement, a financial services provider agrees to pay suppliers on behalf of the buyer, allowing suppliers to receive early payment. The buyer then settles the financial institution later, taking advantage of extended payment terms.
2. Dynamic discounting
Dynamic discounting enables buyers to offer suppliers early payment in exchange for a discount on the invoiced amount. The approach incentivizes suppliers to receive compensation ahead of schedule, while buyers benefit from securing early payment discounts.
3. Approved payables finance (APF)
Approved payables finance, or buyer-centric financing, is a program where a financial institution provides funding directly to the buyer. The buyer then utilizes this funding to extend payment terms to their suppliers. It enables buyers to optimize their working capital while ensuring timely supplier payment.
4. Inventory financing
Inventory financing focuses on using the value of inventory as collateral for securing financing. It allows businesses to free up capital in inventory and leverage it for other operational purposes.
5. Receivables purchase
Receivables purchase involves selling accounts receivable to a financial institution at a discount. It provides immediate cash flow to the seller while transferring the responsibility of collecting payments to the financial institution.
6. Supply chain financing platforms
With the advancement of technology, logistics financing platforms have emerged as efficient solutions. These digital platforms connect buyers, suppliers, and financial institutions, streamlining the process. They offer transparency, automation, and real-time tracking of transactions.
Read More: 10 Best Accounts Payable (AP) Software
Key concepts and components of supply chain finance
Let’s explore four essential concepts and components in detail:
1. Working capital management
It involves efficiently managing the cash and resources required for day-to-day operations. Supply chain programs play a vital role in optimizing working capital by allowing businesses to extend payment terms to suppliers. It frees up cash that would otherwise remain tied up in accounts payable.
2. Supplier financing
Supplier financing enables suppliers to access early payment for their invoices to ensure a stable cash flow and improved liquidity. Collaborating with financial institutions or third-party lenders allows buyers to extend payment terms to suppliers while offering them the option to receive early payment.
3. Buyer financing
Buyer financing involves financial arrangements that allow buyers to optimize their working capital. It does so by extending payment terms while ensuring timely payment to suppliers. Buyers may collaborate with financial institutions to secure funding or leverage their financial capabilities to extend payment terms.
4. Inventory financing
Inventory financing addresses the challenge of managing inventory-related costs and optimizing cash flow. Using inventory as collateral allows businesses to secure financing to fund their inventory needs.
Quick read: 8 Best Inventory Management Software in 2023
How does supply chain finance work?
Logistics financing leverages the financial strength of buyers to provide early payment options or financing to their suppliers. The process involves three key parties:
- Buyers
- Suppliers
- Financial institutions
The buyer extends payment terms to the supplier, allowing them to receive payment later than the agreed-upon invoice date. The supplier, facing a cash flow gap, can receive early compensation from a financial institution at a discounted rate. The financial institution, in turn, pays the supplier upfront and collects the full payment from the buyer at a later date.
The arrangement helps optimize the buyer and supplier cash flow, improves working capital management, and strengthens the buyer-supplier relationship.
Read More: Capital Investment: Meaning, Types, How it Works & Examples
Steps involved in the supply chain finance process
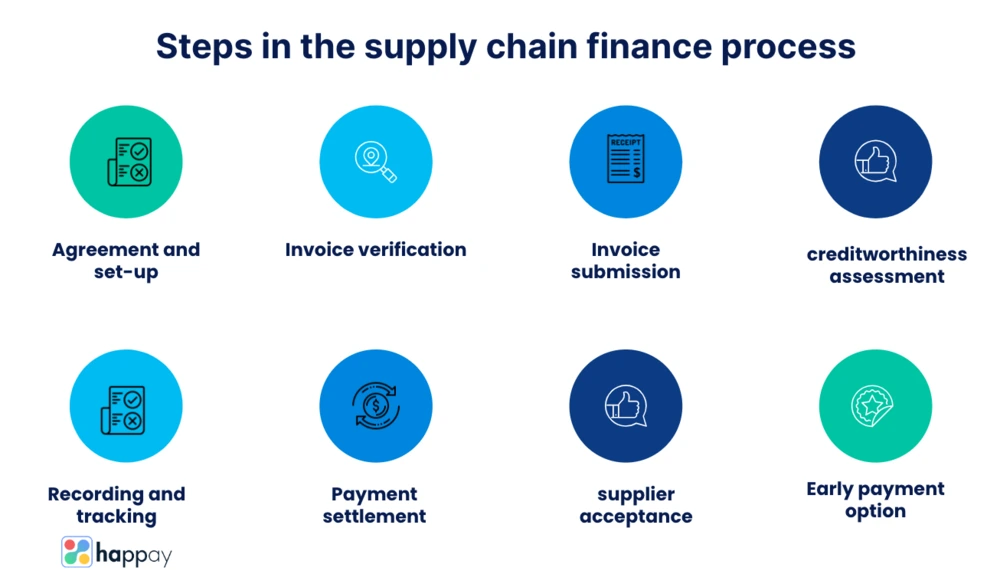
The process involves the following steps to ensure smooth execution and seamless financial transactions.
- Agreement and setup
The buyer, supplier, and lender involved in the program enter into agreements that outline the terms and conditions of the arrangement. It includes establishing the payment terms, discount rates (if applicable), and other relevant details that may be bound by a contract.
- Invoice verification
When the supplier delivers goods or services to the buyer, they generate an invoice reflecting the agreed-upon terms. The buyer verifies the accuracy and validity of the invoice, ensuring it aligns with the terms of the finance program.
- Invoice submission
Once verified, the supplier submits the invoice to the financial institution or service provider facilitating the finance program. The step can be done through a digital platform or by sending the invoice via secure channels.
- Creditworthiness assessment
The financial institution or funder assesses the buyer’s credit rating and validates the invoice details. They evaluate the buyer’s payment history and financial stability.
- Early payment option
If the invoice meets the requirements and passes the credit limit assessment, the financial institution offers an early payment option to the supplier. It may involve paying a portion of the invoice amount in advance.
- Supplier acceptance
The supplier reviews the early payment offer and decides whether to accept it. If accepted, they receive early payment from the financial institution, improving their cash flow and liquidity.
- Payment settlement
The buyer settles the invoice with the financial institution or service provider at the predetermined payment due date.
- Reporting and tracking
Throughout the process, stakeholders have access to real-time reporting and tracking of transactions. It provides visibility into payment statuses, early payment offers, and financial metrics, enabling effective monitoring and analysis.
Example of supply chain finance
One of the largest retail chains globally, Walmart implemented a supply chain financing program in collaboration with HSBC Bank in 2019. The program supports its international trade suppliers and optimizes its cash flow. Through this program, Walmart offers its suppliers access to improved financing.
Walmart provides a valuable financing solution to its suppliers by leveraging its strong creditworthiness and financial position. It allows them to access liquidity and improve their cash flow. The program for global trade benefits both Walmart and its suppliers, strengthening their relationship. It also provides financial stability to suppliers and ensures a steady supply of goods for Walmart’s retail operations.
Read More: Cash Flow Statements: A Comprehensive Guide
Advantages and disadvantages of supply chain finance
Let’s explore the advantages and disadvantages of supply network finance:
Advantages of supply chain finance
- Improved cash flow and working capital management: Supply network finance helps businesses optimize their cash flow by aligning payment terms with cash conversion cycles. It improves working capital management and frees up cash for growth initiatives or other operational needs.
- Enhanced supplier relationships: Supply network finance programs enable buyers to offer early payment options to suppliers, which can strengthen relationships and foster trust. Providing suppliers with reliable cash flow helps businesses maintain solid partnerships and negotiate favorable terms.
- Access to cheaper financing: For suppliers, logistics finance offers an alternative to bank loans, which can be costly. Leveraging supply network finance programs allows suppliers to access financing at favorable rates.
- Risk mitigation: Supply network finance can help mitigate the risk of non-payment or delays in payment. Buyers ensure suppliers receive timely payment by providing early payment options.
Disadvantages of supply chain finance
- Potential cost to suppliers: While logistics finance can be advantageous for buyers, suppliers may incur costs in the form of discounts or fees associated with early payment. These costs need evaluation to ensure the benefits outweigh them and do not strain the financial health of suppliers.
- Dependency on financial institutions: Implementing a supply network finance program involves partnering with financial institutions or service providers. The dependence on external parties introduces additional complexity and requires trust in the financial institution’s capabilities and reliability.
- Program implementation challenges: Establishing a logistics finance program requires coordination and agreement between buyers, suppliers, and financial institutions. This can involve administrative complexities, contractual negotiations, and integration with existing systems or processes, which may present implementation challenges.
- Potential impact on relationships: While supply network finance can strengthen relationships, it is essential to manage the program to balance the financial interests of buyers and suppliers. In some cases, the implementation of such programs can strain relationships if not handled carefully, particularly if suppliers perceive the program as disadvantageous or burdensome.
Learn about: 10 Best Finance Software for Personal and Business in 2023
Supply chain finance techniques and tools
Supply network finance encompasses the following techniques and tools to optimize financial operations and strengthen global supply chain relationships:
1. Invoice discounting
Invoice discounting allows businesses to access immediate funds by selling their accounts receivable to a financial institution at a discount. The technique helps improve cash flow by converting outstanding invoices into cash, allowing businesses to meet their financial obligations.
2. Dynamic discounting platforms
Dynamic discounting platforms enable buyers to offer early payment discounts to suppliers in exchange for prompt payment. These platforms facilitate the negotiation and execution of discount terms, promoting cash flow optimization for buyers and suppliers. They provide a centralized and automated platform for managing early payment options.
3. Electronic data interchange (EDI)
EDI is a tool that enables the exchange of business documents electronically between trading partners. It streamlines invoice submission and processing, reducing manual intervention and improving efficiency. EDI enhances accuracy and speeds up payment processing.
4. Supply chain finance platforms
Logistics financing platforms connect buyers, suppliers, and financial institutions. These platforms streamline the process by automating invoice submission, credit assessments, payment processing, and reporting.
Learn more: Order to Cash (O2C) Process: A Step-by-Step Approach
Key objectives and benefits of implementing supply chain finance solutions
Implementing logistics financing solutions can offer the following benefits:
1. Improve cash flow management
Extending payment terms or offering early payment options to suppliers allows businesses to manage their cash conversion cycle. It ensures a healthy balance between incoming and outgoing cash flows. Organizations get improved working capital and supply chain management for increased financial stability.
2. Strengthen supplier relationships
Organizations demonstrate their commitment to supporting their suppliers’ financial well-being by providing them access to early payment. It helps build trust, promotes collaboration, and enhances the reliability of the supply chain network.
3. Enhance operational efficiency
Automating invoice submission, credit assessments, and payment processing helps businesses reduce manual intervention and minimize errors. It enables finance teams to focus on strategic procurement instead of administrative tasks.
4. Optimize working capital
Logistics financing solutions contribute to optimizing working capital by effectively managing payment terms. Companies can extend payment cycles, allowing them to utilize their cash resources more efficiently.
5. Mitigate supply chain risks
Organizations reduce the risk of disruptions caused by financial instability among suppliers by offering early payment options. It contributes to a more stable and reliable supply chain, minimizing the impact of potential troubles.
6. Gain a competitive advantage
Companies that effectively manage their cash flow strengthen supplier relationships and optimize working capital. They gain a better position to respond to market dynamics and differentiate themselves from competitors. The ability to offer attractive payment terms to suppliers is valuable in attracting and retaining top-tier suppliers.
Read about: Vendor Management: What is it, Types, Process and Tools
Implementing supply chain finance programs
Let’s explore the critical steps involved in implementing logistics financing programs:
1. Assess business needs
Start by assessing your business’s financial objectives, cash flow challenges, and supply chain dynamics. Identify areas where logistics financing can add value and address specific pain points. Determine the scope and scale of the program based on the size of your supplier base and transaction volumes.
2. Identify suitable partners
Seek financial institutions with expertise in logistics finance. Evaluate their reputation, track record, range of services, and compatibility with your business requirements. Choose partners who can offer the right finance products and technology solutions.
3. Establish program structure and guidelines
Define your supply chain financing program’s structure, terms, and guidelines. It includes determining payment terms, early payment options, discount rates, credit assessment criteria, and other relevant parameters.
4. Engage stakeholders
Engage with suppliers, buyers, finance teams, and IT departments to foster understanding and gain their support. Communicate the benefits and objectives of the supply network finance program. Furthermore, encourage open dialogue and collaboration to ensure a smooth implementation process.
5. Integrate technology platforms
This step involves leveraging technology platforms for seamless transaction processing and reporting. Integrate these platforms with your existing systems or adopt new ones to enable efficient invoice submission, credit assessment, payment processing, and real-time tracking of transactions.
6. Conduct pilot testing
Consider conducting a pilot test of the logistics financing program with select suppliers and buyers. It will allow you to evaluate the program’s effectiveness, identify operational challenges, and make necessary adjustments before scaling up. Gather feedback from participants to fine-tune the program.
7. Roll out and monitor
Once the pilot testing is successful, roll out the logistics financing program to a broader group of suppliers and buyers. Monitor the program’s performance, track key metrics, and impact on cash flow.
8. Provide ongoing support and communication
Offer ongoing support to suppliers, buyers, and other stakeholders involved in the supply network finance program. Address inquiries, provide training, and keep participants informed about program updates.
Read about: Procurement KPIs Guide: Top 10 Metrics to Measure Your Success
Challenges and considerations in implementing supply chain finance
Let’s explore some key points to keep in mind when implementing logistics financing:
1. Complexities in coordinating financing across multiple stakeholders
Supply chain financing involves coordinating financing arrangements between buyers, suppliers, and financial institutions. Managing the diverse needs and expectations of these stakeholders can be complex. It is essential to establish clear lines of communication, streamline processes, and ensure alignment among all parties involved.
2. Mitigating risk and ensuring trust among supply chain partners
Supply network finance involves sharing financial information and potentially relying on the creditworthiness of suppliers. Mitigating risk and building trust among supply chain partners are critical considerations. Implement robust risk assessment frameworks and due diligence processes to safeguard financial interests.
3. Integrating supply chain finance with existing systems and processes
The process can be challenging when dealing with legacy systems or complex IT architectures. Ensure that the logistics financing program seamlessly integrates with the existing infrastructure and workflows used by buyers and suppliers.
Here’s a quick read on: Sourcing vs Procurement: A Complete Guide On Key Differences
Bottom line
Understanding logistics financing is essential for businesses aiming to optimize cash flow and strengthen supplier relationships. Leveraging the proper techniques, tools, and strategies will help your organization navigate the complexities of logistics financing. Furthermore, it will allow you to unlock its potential to drive financial stability and promote growth in the hyper-competitive business landscape.
FAQs
Supply chain financing is a financial solution that helps businesses optimize cash flow by extending payment terms to their suppliers. An example is when a large retailer agrees to pay its suppliers within 60 days instead of the usual 30 days but offers them the option to receive early payment from a financial institution at a slight discount.
Supply chain financing is beneficial for both buyers and suppliers. Buyers who want to optimize their working capital and improve cash flow can benefit from the program. Similarly, suppliers who face cash flow challenges and need access to liquidity can benefit from early payment options.
The interest rates for supply chain financing can vary depending on the creditworthiness of the buyer, the supplier’s risk profile, the program structure, and the financial institution involved. The interest rates for supply chain financing can be competitive compared to other financing forms due to the buyer-supplier relationship’s underlying strength.
Blockchain technology can enhance supply chain finance by providing transparency, traceability, and security throughout the supply chain. It enables the creation of a decentralized and immutable ledger, which allows real-time visibility into transactions and inventory movements.
Supply chain finance differs from traditional lending in several ways. Traditional lending typically focuses on the borrower’s creditworthiness and involves collateral requirements and lengthy approval processes. In contrast, supply chain finance considers the buyer’s creditworthiness and involves financing the supplier’s receivables or providing early payment options. It leverages the buyer’s more robust credit profile and the buyer-supplier relationship to offer favorable terms and reduce the risk for both parties.







