Sourcing and Procurement
A supply chain is a competitive advantage that many enterprises ignore until something is broken.
According to Zumen, 69% of organizations don’t have total visibility on their supply chain. Supply chain optimization enables such enterprises to maintain optimal inventory levels, reduce overhead costs, and boost business profits.
Organizations aiming to improve supply base efficiency start by refining sourcing and procurement activities.
Sourcing and procurement are two distinct supply chain management processes, despite the synergy between them. Product sourcing is part of the procurement lifecycle, whereas procurement is a holistic process of obtaining goods and services for operations. While many use these two terms interchangeably, they aren’t the same.
In this article about sourcing vs procurement, we explore the differences between sourcing and procurement and how integrating both can be beneficial for organizations.
Also, Read: What is Source-to-pay (S2P)?
Sourcing
Definition and explanation of sourcing
Sourcing refers to the business process of identifying, vetting, choosing, and managing suppliers that provide the best value for an organization. It involves extensive vendor management and finding reliable vendors to provide high-quality products in the right quantities while meeting an organization’s compliance policies.
Sourcing includes the following activities:
- Requesting quotes
- Gathering supplier information
- Finding out the lead time
- Contract management and negotiation
- Reviewing pricing terms and minimum order quantities (MOQs)
The goal of sourcing is to ensure an organization has access to the necessary resources for meeting business objectives. Strategic sourcing also enables sourcing teams to maintain strong supplier relationships over a period.
Importance of effective sourcing
Effective sourcing aids organizations in reducing overhead costs, meeting market demands, and controlling inventory levels for optimal production. It also improves the supply chain efficiency of enterprises.
- Lower prices of goods and services with negotiation
- Ensure supply stability with strong vendor partnerships
- Reduce supply chain risks with timely conflict resolution
- Improve supply chain management efficiency
Benefits of sourcing
Enterprises streamlining sourcing activities enjoy the following benefits.
- Shortened sourcing timelines
- A steady supply of quality raw materials
- Improved cost-savings on goods and services purchases
- Strong supplier relationships for favorable contract terms
- Efficient supply chain risk analysis with vendor intelligence
- Improved ability to meet regulatory and compliance guidelines
Features of sourcing
Efficient sourcing improves organizations’ profit margins and competitiveness with the following features.
- Market research for finding suppliers
- Contract negotiation
- Setting payment terms and conditions
- Goods and services quality testing
- Exploring outsourcing opportunities
Suggested Read: Centralized vs Decentralized Purchasing
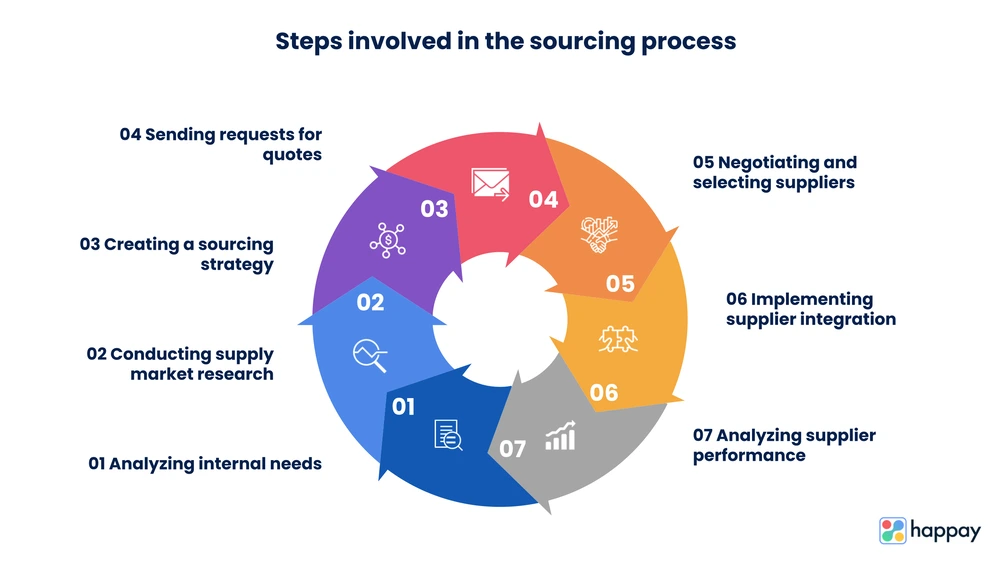
Steps involved in the sourcing process
Although the steps of the sourcing process vary depending on organizational structure, most enterprises adhere to the following steps.
- Analyzing internal needs
- Conducting supply market research
- Creating a sourcing strategy
- Sending requests for quotes (RFQs), requests for proposals (RFPs), and requests for information (RFIs) for vetting suppliers
- Negotiating and selecting suppliers
- Implementing supplier integration
- Analyzing supplier performance
1. Analyzing internal needs
The process starts with the sourcing team identifying their organization’s goods and services requirements. The team also gathers other related information, such as
- Spend category
- Spending limits
- Current item prices
- Product specifications
- Product users and their departments
These key details provide sourcing managers with a holistic understanding of organizational needs.
2. Conducting supply market research
Now, sourcing specialists research suppliers who can meet an organization’s specific needs. Researching the supply market enables sourcing teams to assess market risks, offerings, and opportunities. They also compare product component costs with raw material, labor, and transportation costs that form a basis for future decision-making.
3. Creating a sourcing strategy
The third step involves creating a plan of action for obtaining supplies at the lowest prices. This plan helps sourcing departments decide where to buy goods, how to ensure supply chain stability and ways to minimize risks. The sourcing strategy also enables stakeholders to set the criteria for choosing potential suppliers.
4. Sending RFQs, RFPs, and RFIs for vetting suppliers
Now, organizations send requests for quotes (RFQs), information (RFIs), or proposals (RFPs) to potential suppliers. This step evaluates vendors based on their bids, which contain project details, pricing, delivery terms, and product specifications.
5. Negotiating and selecting suppliers
At this stage, the sourcing team shortlists suppliers based on product quality, prices, payment terms, and possible risks. The team also negotiates with these vendors for better terms and mutual benefits. Ultimately, an organization chooses reputed vendors offering the best price for high-quality products.
6. Implementing supplier integration
The supplier integration process begins once an organization notifies the selected vendors. Suppliers sign contracts and review the supplier performance guidelines at this stage.
7. Analyzing supplier performance
The final stage of performance benchmarking happens after suppliers deliver goods and services. At this stage, the sourcing team measures suppliers’ performance against predefined KPIs and metrics.
Recommended Read: Vendor Payment System (VMS)
Procurement
Procurement is the end-to-end process of planning purchases, placing orders with suppliers, confirming orders, paying suppliers, inspecting delivered goods, and recording purchases. It starts with identifying goods and services needs and ends only after fulfilling those needs.
Definition and explanation of procurement
Enterprises use procurement strategies as a long-term plan to align their purchasing and spending goals with their supply chain objectives.
An effective procurement strategy is key to obtaining the goods and services necessary for running day-to-day operations. Organizations adopting strategic procurement approaches can efficiently save money, build mutually beneficial supplier relationships, and optimize supply chains.
Importance of effective procurement
Procurement is a strategic function that enterprises use to manage inventory-related costs and source raw materials efficiently. It’s important because of the following reasons.
- Directly impacts the bottom line
- Boosts supply chain risk management capabilities
- Improves profit margins
- Establishes relationships with suppliers
The next section explores how procurement benefits enterprises.
Benefits of procurement
Effective procurement management offers the following benefits.
- Reduced supplier risks
- Lowered raw material costs
- Increased process transparency
- Improved supply management resiliency
- Enhanced resource availability
Features of procurement
Procurement makes it easier for organizations to identify needs, source supplies, and pay suppliers. Here are the salient features of procurement.
- End-to-end purchase management
- Improved supplier lifecycle management
- Spend analysis for budget control
- Purchasing data insights for decision-making
Related Read: What is P2P Cycle: Procure-to-Pay Process
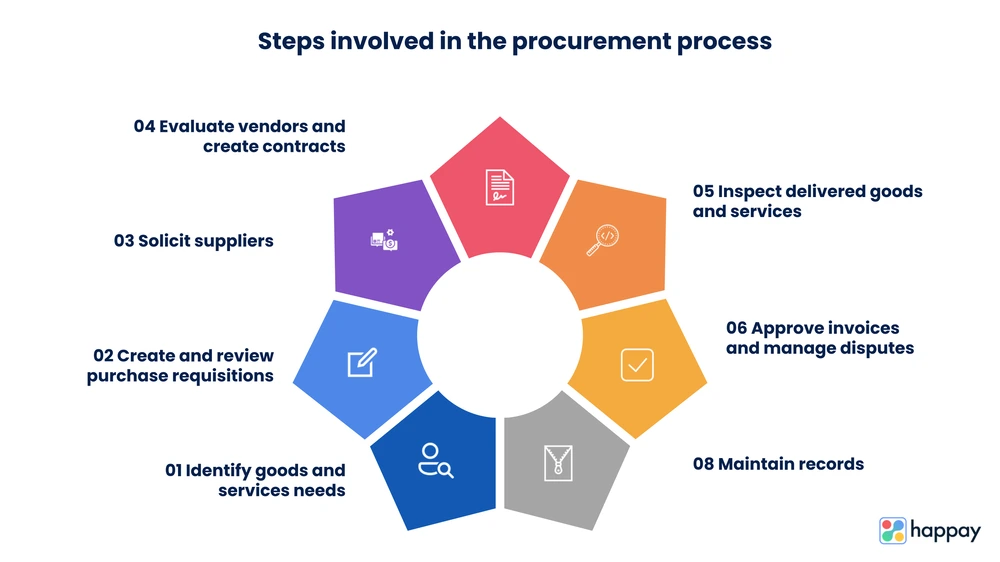
Steps involved in the procurement process
The procurement process involves multiple stages, including needs identification, purchase request creation, payment fulfillment, and more. Below are the seven steps that organizations follow during procurement.
- Identify goods and services needs
- Create and review purchase requisitions
- Solicit suppliers
- Evaluate vendors and create contracts
- Inspect delivered goods and services
- Approve invoices and manage disputes
- Maintain records
1. Identify goods and services needs
The first stage of the procurement process involves identifying the company’s needs. Establishing these needs upfront helps enterprises create effective procurement plans.
2. Create and review purchase requisitions
The procurement process begins when users in the organization create purchase requisitions to meet existing demands. Procurement departments approve these requisitions after checking budget availability with department heads. The review process also involves managers reviewing the actual need for requested goods and services.
3. Solicit suppliers
Now, the procurement team approves requisitions and starts the supplier solicitation process. At this point, they generate purchase orders (POs) and create a procurement plan specific to the requirements. Based on the plan, they share a request for quotes (RFQ) and a request for proposal (RFP) with each potential vendor. The goal of this stage is to find the best from all bids submitted by providers.
4. Evaluate vendors and create contracts
Next, the procurement professionals review quotations they received during the last stage. Once they find the best suppliers, they start the negotiation process for more favorable terms. At the end of this stage, suppliers sign legally binding contracts with organizations. Then they receive POs and start delivering goods.
5. Inspect delivered goods and services
This step involves the purchasing team physically inspecting the material delivered. They generate good receipt notes (GRNs) after confirming quantity and quality. In the event of non-compliance, the procurement team documents the issue and notifies the supplier.
6. Approve invoices and manage disputes
Vendors share supplier invoices with the buying team after resolving delivery issues. Now, the onus is on the procurement and accounting team to verify POs, supplier invoices, and delivery receipts with three-way matching. The accounts payable team processes payment for approved invoices.
7. Maintain records
With a focus on vendor management, organizations meticulously record all invoices, supplier invoices, and order receipts after processing vendor payments. These documents help them with future auditing and bookkeeping.
Also, Read: 10 Best Procurement Software
Key differences between sourcing and procurement
The key difference between sourcing and procurement is that: sourcing focuses on finding and vetting suppliers, whereas procurement also considers the actual purchasing part.
Sourcing involves finding high-quality products through third-party suppliers, partnerships, or joint ventures. On the other hand, procurement happens directly with suppliers through distributors, commercial agents, and brokers.
Sourcing vs Procurement
The sourcing vs procurement table below explores the key differences between them.
Sourcing |
Procurement |
|
|
Meaning |
The process of finding suitable sources for obtaining goods and services. |
The process of obtaining goods and supplies through bidding, direct purchasing, or tendering. |
|
Goal |
To minimize sourcing costs while optimizing supply chain efficiency. |
To gain a competitive advantage while meeting internal needs. |
|
Objective |
To find out who will provide supplies. |
To answer what kind of supplies will be obtained. |
|
Focus |
Finding suitable vendors and negotiating contract terms |
Obtaining high-quality goods for meeting organizational needs |
|
Approach |
Strategic |
Both strategic and tactical |
|
Vendor relationship |
Creates strong relations with suppliers and vendors |
Manages supplier relationships for mutual benefits |
Why do the differences matter?
Understanding sourcing vs procurement is essential for purchasing goods and services efficiently. These two processes are closely related yet not the same. Knowing their differences is key to understanding their roles in the broader purchasing workflow.
Sourcing is a process that organizations use to locate outside suppliers for obtaining products and services. Procurement helps them negotiate contracts with these suppliers and get the best prices.
Quick Read: CapEx vs. OpEx
Benefits of integrating sourcing and procurement
Integrating sourcing and procurement allows organizations to find reliable suppliers, forecast purchasing costs accurately, and save money. Moreover, both teams can collaborate efficiently with sourcing and procurement data in one place.
Here are some of the benefits organizations experience after connecting sourcing and procurement.
- Improved spend visibility
- Enhanced communication
- Better supplier management
1. Improved spend visibility
Connecting sourcing and procurement streamlines purchase order tracking. As a result, organizations can easily prevent unapproved purchases or over-budget spending. For example, organizations can integrate sourcing and procurement to aggregate demand and avoid duplicate purchases across departments.
2. Enhanced communication
Organizations integrating sourcing and procurement also prevent miscommunication. For example, if a vendor promises a 15% discount during sourcing, the procurement team isn’t likely to know about it. Setting up a communication plan helps both teams maximize the exchange of information.
3. Better supplier management
Sourcing teams learn more about each supplier’s capability and credibility during the vetting process. Procurement teams evaluate these suppliers based on their goods and prices.
Integrating sourcing and procurement allows both teams to be aware of each supplier’s role in business continuity and organizational performance. For example, once a sourcing team finds suppliers that align with organizational values, a procurement team can work on getting the best deal from those suppliers.
Also, Read: What is Spend Analytics in Procurement?
Conclusion
Sourcing and procurement are two related but different processes. Sourcing is a part of the broader procurement function. It aims to help organizations find favorable suppliers offering the lowest prices.
On the other hand, procurement includes all purchase-related activities. Instead of sourcing vs procurement, you must integrate the processes as it enables organizations to prevent supply disruption and optimize supply chain efficiency.
FAQs
Sourcing is the process of finding suitable vendors for purchasing goods and services. Procurement is the process of obtaining products from these vendors for internal needs. In sourcing vs procurement, the key difference is that sourcing focuses on finding and vetting suppliers, whereas procurement enables an organization to meet demands with timely supplies.
Sourcing comes first and is a subset of procurement. Procurement teams can’t obtain goods and services until the sourcing team finds and verifies suppliers.
The different types of sourcing are:
Insourcing
Outsourcing
Near-sourcing
Low-cost country sourcing (LCCS)
Global sourcing
Subcontracting agreements
Captive service operations
Professional service
Manufacturing
Vertical integrations
Few suppliers
Joint ventures
Virtual enterprises
The sourcing process involves all activities related to finding suppliers, evaluating them, and creating contracts with those who offer the best value.
A vendor is an individual or an organization that purchases products from manufacturing units and sells them to customer entities. A supplier is an enterprise business or a person who provides organizational manufacturing units with raw materials, machines, and parts.
The process of procurement refers to all activities related to sourcing suppliers, obtaining goods from them, inspecting deliveries, matching supplier invoices, and processing payments.
Procurement is the process of sourcing vendors, acquiring goods, and paying them. It plays a key role in helping organizations meet market demands and run daily operations.


Discussion about this post